How AI Is Used In War Today
30 September 2024
From autonomous drones to facial recognition algorithms designed to recognize perpetrators of war crimes, the conflict in Ukraine has become a testing ground for the use of artificial intelligence in warfare.
Much of this technology has been provided by Western companies. Just as David triumphed over Goliath thanks to his technological advantage, the hope is that their support will give Ukraine an advantage over its far larger Russian opponent.
From the bow and arrow to the atomic bomb, war has always been a key driver of technological advancement. But with one U.S. general describing its impact in Ukraine as “the most significant fundamental change in the character of war ever recorded in history,” let’s take a look at what it might mean for the way conflicts are fought and won in the future.
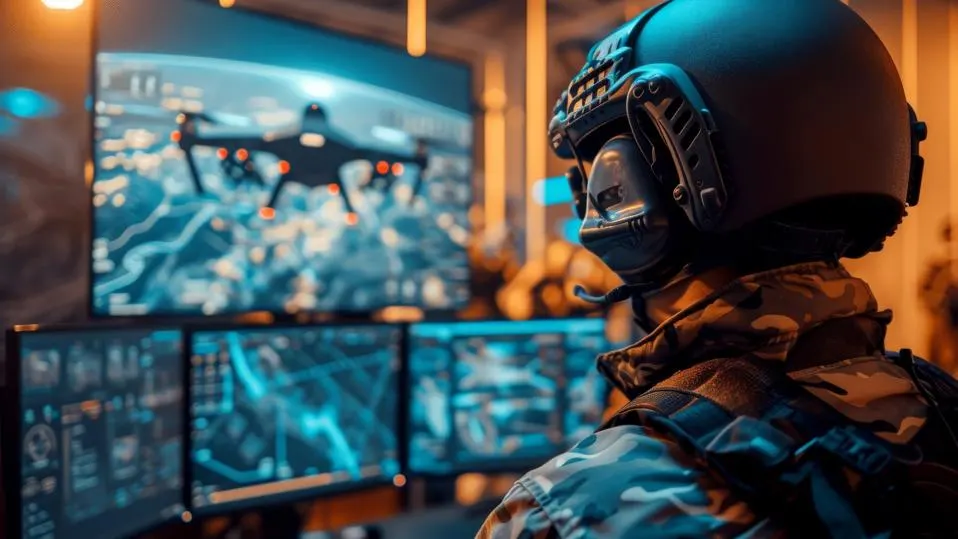

How Is Being AI Used In Ukraine?
The Ukrainian government has put technology in general — and AI in particular — on the front line of its war strategy since the start of the conflict in 2022.
When war broke out in the country where 300,000 are employed in the tech sector, many startups pivoted to development that would aid the war effort.
The government even set up a funding platform, Brave1, to allow companies to pitch defense technology products to investors. It is reported to have received thousands of submissions.
One of the major breakthroughs we’ve seen in Ukraine is the use of autonomous drones. While unmanned aerial vehicles have been used in many conflicts in the past decade, these are usually piloted by humans remotely. Today, in Ukraine, drones have reportedly been used that are capable of tracking and engaging enemies without human interaction — in other words, true killer robots.
There’s also BAD One, a dog-like autonomous robot designed by British company Alliance, which moves stealthily through combat zones and detects enemy placements as well as minefields using thermal vision. It can also carry ammunition to resupply soldiers while they are engaged in fighting.
And the Ukrainian military has also demonstrated the use of an autonomous machine gun, which reportedly uses AI to spot and target enemies moving in the field.
Not all the AI being used in Ukraine is focused on defeating the enemy; there are humanitarian use cases, too.
AI is being used to help with the resettlement of refugees and people displaced by conflict by tracking the condition of roads and infrastructure and monitoring supply routes used for delivering food and essential supplies.
It’s also used to analyze siloed data streams that give clues that can help with clearing landmines in what has become the most heavily mined country in the world.
Elsewhere, AI is helping to collect evidence that could help hold those who commit war crimes to account. Allegations and reports are linked to satellite imagery showing troop movements, and videos are uploaded to social media to build cases for future prosecutions.
And facial recognition technology, supplied by U.S. company Clearview, has been used to identify Russian soldiers crossing the border, to make it easier to trace and hold them to account in the aftermath.
The Ethics Of AI In Warfare
Of course, all of this raises many ethical questions. Should tech companies, for any reason, be developing tools that openly go against the principles of “harmless” AI?
Palantir, a data analytics company, has reportedly been linked to military applications. The company has faced scrutiny in the past over its involvement in surveillance technology. More recently, some reports have suggested that Palantir's tools may have been utilized in Ukraine's AI-augmented surveillance efforts during the ongoing conflict, though these claims have not been independently verified.
The potential use of such technologies in war zones raises broader concerns about their future applications. If these tools are indeed being deployed in military contexts, is there a risk they could eventually find their way into civilian settings? This possibility, while speculative, merits careful consideration and robust public discourse.
A big question is if it is ever ethically justified to allow machines to make the decision to kill. Ukraine’s AI machine gun technology, for example, is capable of identifying targets as enemies but still requires a human operator to authorize it to fire. But will this always be the case?
And while the robot dogs mentioned above are reportedly used for reconnaissance and resupply, China has demonstrated a similar technology equipped with a machine gun and capable of engaging in combat.
There’s also a risk of overemphasizing the role of AI and technology in warfare. Though it can certainly provide material for propaganda and perhaps cause fear among the enemy, it shouldn’t be forgotten that the vast majority of fighting and killing is still being done by humans, up to their knees in mud with the sound of artillery ringing in their ears.
Underplaying the horror and danger of their situation by portraying the war in Ukraine as being fought mainly by robots and software risks “tech-washing” the brutality of warfare.
AI And The Future Of War
History tells us that any rules or principles of fair play often prove inconsequential in warfare. While, from what we have seen, AI in Ukraine seems to stop short of actually killing people, we know that technology that crosses that red line is under development.
Some might say that robotic warfare could potentially save human lives by avoiding the need to put humans into combat zones in the first place. But what happens when one side runs out of robots? Do they surrender or start sending people into the fray?
Advances made in AI warfare in Ukraine remind us that technological and ethical developments don’t always progress at the same speed. While AI might reduce human casualties, it also raises stark questions about the level of power and autonomy that we’re willing to hand over to robots. How we answer those questions could have big implications for how AI impacts society during peacetime and war.
Related Articles
Flying Taxis And Self-Driving Trucks Arrive In 2026: 6 Transport Trends To Watch
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
Technology in Action: My Key Takeaways on How AI and Quantum Are Accelerating Global Transformation
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
Sign up to Stay in Touch!
Bernard Marr is a world-renowned futurist, influencer and thought leader in the fields of business and technology, with a passion for using technology for the good of humanity.
He is a best-selling author of over 20 books, writes a regular column for Forbes and advises and coaches many of the world’s best-known organisations.
He has a combined following of 4 million people across his social media channels and newsletters and was ranked by LinkedIn as one of the top 5 business influencers in the world.
Bernard’s latest book is ‘Generative AI in Practice’.





Social Media