The Best Examples Of Human And Robot Collaboration
22 August 2022
The future of work is not about humans being replaced by robots. Rather, it is about us learning to work alongside smart, automated technology that will augment our capabilities while allowing us to focus on skills that are uniquely humans.
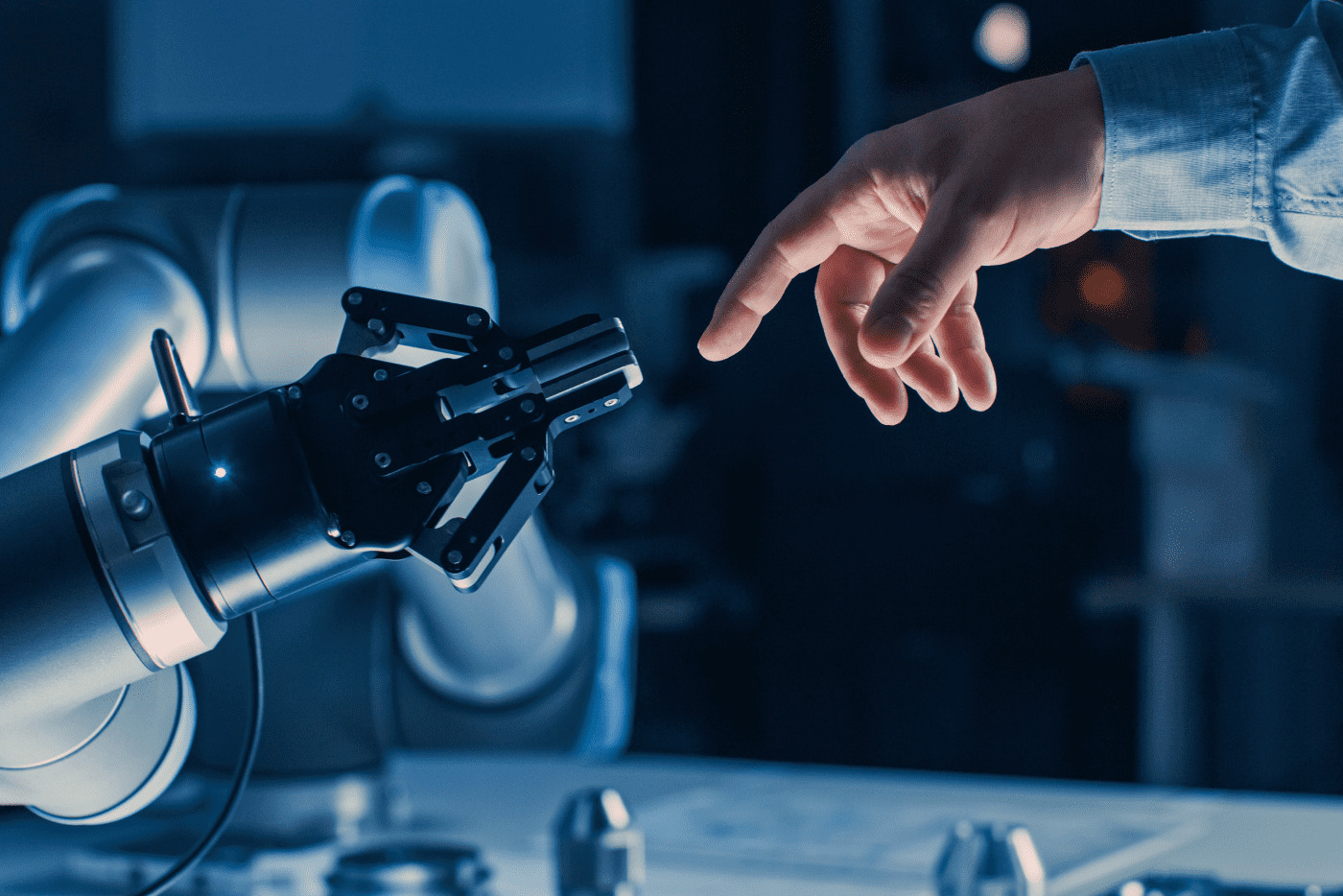

We have been sharing our workplaces with robots for some time now – the earliest industrial robots were used in the mid-20th century, usually to carry out routine, manual assembly work on production lines. What makes today’s industrial robots different is that they are capable of carrying out work in a way that is truly autonomous, without needing direct control or input from us to tell them how to do it. This is because they are controlled by artificial intelligence (AI) – specifically software algorithms that use machine learning to enable them to continuously get better and better at their jobs.
If, as is true of many of us, your concept of what a robot is comes from science fiction, then many of today’s industrial robots may not look quite as you expect them to. This is because they are generally built to carry out one particular task, so they will often look pretty similar to whatever regular, non-AI machine is usually used for that job. The term “robot” is also sometimes used to refer to autonomous systems that are entirely built-in software, as in Robotic Process Automation (RPA).
Warehouse Robots
A famous example of human and robot collaboration is Amazon's warehouse robots that work alongside staff in its fulfillment centers. These robots have one job – to bring items to human pickers so they can be packaged and labeled for dispatch. They do this by moving entire shelving units and are programmed to watch out for humans so they will not collide and cause accidents. While the existing robots are limited to working in certain designated areas, a newer model currently being trialed, nicknamed "Bert," will be able to safely navigate anywhere on the factory floor. Amazon says that since it introduced robots to its warehouses in 2012, it has also created over a million human jobs.
Agricultural Robots
Robots are often used to work on farms to carry out jobs that are dangerous or just boring. Autonomous drones can be used to plant seeds, spread fertilizers and pesticides, and watch out for invasive species or trespassers. Humans will oversee their work and step in when manual decisions need to be made. US startup Burro creates “people scale” collaborative robots (or “cobots”) that use computer vision and GPS to follow agricultural workers and assist them with day-to-day work. The market for robots in agriculture is predicted to be worth $11.58 billion by 2025.
Healthcare Robots
Moxie is a cobot created by Diligent Robots designed to help nurses and other staff on their rounds in hospitals. It can make deliveries and carry out a number of non-clinical tasks proactively, such as restocking supplies and collecting samples. It can do this without needing to be told precisely what to do, by integrating with electronic healthcare records. The idea is that robots like Moxie will leave human workers free to carry out the parts of their job that can be best done by humans, like providing care and compassion to the sick.
Wellbeing and Therapy Robots
Robots are increasingly used to help patients recovering from injury or surgery. The collaborative robots created by Italian startup Heaxel train those in recovery to carry out repetitive movements, monitor their progress towards recovery, and pass data back to human therapists who are able to use it to fine-tune the recovery program. Other robots have been created that are designed to live alongside the elderly or disabled. As well as providing a form of companionship, they assist caregivers by monitoring their wellbeing and watching out for accidents and falls in the home.
Military Robots
A robot called RoMan has been used by the US Army to clear roads of obstacles that may be providing cover for enemies, or other hazards such as improvised explosive devices. It uses 3D sensor data to determine whether objects will pose an obstacle or a hazard, a pair of mantis-like arms originally designed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and is powered by deep learning algorithms.
Manufacturing Robots
So, robots have now gone full-circle and ended up back where they started, in manufacturing. But today’s collaborative manufacturing robots are significantly more advanced than they were when General Motors installed its first robots at its New Jersey plant in 1962. Symbio Robotics creates robots that are used by car manufacturers, including Ford and Toyota, not just for welding and spray painting but for installing components, picking parts, testing systems, checking for faults or defects, and screwing and bolting. These processes constitute the part of the manufacturing cycle known as “final assembly," which traditionally is the most complex and difficult to automate. This is because they require a greater degree of precise control and manual dexterity, which hasn’t been available in robotic systems until recently.
Kitchen Robots
Fast-food chains have been quick to adopt automation in their drive to increase service speed and bring down operating costs. Miso Robotics has created a kitchen cobot that has been trialed by companies including Caliburger and Walmart, as well as at the Dodger Stadium. The robot, known as flippy, assists human chefs by flipping burgers and frying chicken, and unlike human chefs is capable of working for 100,000 hours without a break.
Related Articles
Flying Taxis And Self-Driving Trucks Arrive In 2026: 6 Transport Trends To Watch
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
Technology in Action: My Key Takeaways on How AI and Quantum Are Accelerating Global Transformation
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
The 10 Biggest Consumer Technology Trends Of 2026
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
8 AI Ethics Trends That Will Redefine Trust And Accountability In 2026
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
The 7 Banking And Fintech Trends That Will Define 2026
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
The 8 Biggest Healthcare Technology Trends To Watch In 2026
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
Sign up to Stay in Touch!
Bernard Marr is a world-renowned futurist, influencer and thought leader in the fields of business and technology, with a passion for using technology for the good of humanity.
He is a best-selling author of over 20 books, writes a regular column for Forbes and advises and coaches many of the world’s best-known organisations.
He has a combined following of 4 million people across his social media channels and newsletters and was ranked by LinkedIn as one of the top 5 business influencers in the world.
Bernard’s latest book is ‘Generative AI in Practice’.









Social Media