The Uncanny Valley: Advancements And Anxieties Of AI That Mimics Life
19 February 2024
Seeing something that looks almost but not exactly human can be a strange and frightening experience for some people. This effect has been known for decades as the uncanny valley. In recent years, though, it has grown in relevance as lifelike robots, movie CG, and digital avatars become features of everyday life.
The term originates in psychology and refers to the steep downward curve of a graph plotting a person’s emotional response to an object as it appears increasingly human. This was discovered during experiments in the seventies that predicted humans would have a very negative emotional response to anything that looks very like a human – but not quite.
So, is this something we will have to deal with more frequently as technology in all forms becomes more and more lifelike? And what problems is it likely to cause in a society where it’s becoming increasingly hard to tell what’s real and what’s virtual?
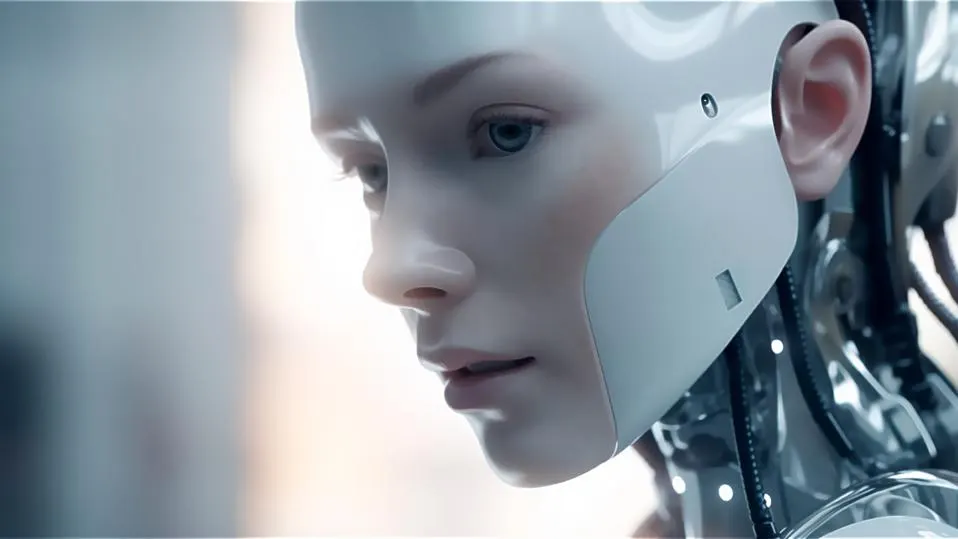
AI And The Uncanny Valley
Robots that we can’t differentiate from humans may still be some way off, although there have been some impressive advances in this field recently, including robots like Ameca that can display human emotions.
Given the speed with which the technology is improving, it isn’t hard to believe that we’ll soon have virtual reality simulations with far higher graphical fidelity than those we see today.
Perhaps most pertinently, however, artificial intelligence (AI) is making it possible to create synthetic human faces, as well as voices, that are closer and closer to being true to life.
Ultimately, this means that as time passes, we’re likely to encounter the uncanny valley phenomenon more frequently.
Implications And Challenges
So why is this a problem?
Well, we’re still far from clear on the impact that growing exposure to realistic, simulated humans and human intelligences will have on our mental health.
For some, the uncanny valley already creates increased emotional discomfort and anxiety. If this scales up as more of us are exposed, it could lead to a widespread breakdown in trust in the technology. For those of us who believe AI has huge potential to do good in the world, this would be a shame.
From the perspective of those who make the technology, anyone spending millions or billions of dollars to design and build robots and AI humans probably isn’t going to want us to feel repulsed by them.
Many of the forthcoming use cases for AI involve applications where it should remove stress and anxiety from the situation rather than add to it, such as healthcare or customer service applications.
So, the challenge will involve balancing functionality – the ability to provide the service we expect from a robot or an AI – with a form that avoids triggering the eerie sensations we’re discussing here.
Conquering The Uncanny Valley
The challenge of creating “acceptable” robots and AI is as much of a psychological and societal problem as it is a technical one.
Overcoming it will likely require cooperation between engineers and those with “soft” human skills in languages, psychology and emotional intelligence.
In robots, digital humans and AI avatars alike, it will involve implementing the subtle, individualistic behaviors we use to communicate qualities like trust and compassion during social interactions.
Impressive as they sometimes are, this is still largely absent from the current generation of synthetic human technology.
Person-to-person interaction is highly complex and nuanced. Everything from body language to voice tone and our experience of a person influences the way we perceive and react to our fellow humans. Robotics engineers and creators of digital human beings are still only scratching the surface when it comes to simulating it.
When we get there, it will likely come down to algorithms that will learn (rather than be programmed) to read and respond to human behaviors in real time, automatically adjusting their actions to match the context of a situation.
Progress is already being made in this field – emotional AI refers to machines that attempt to detect and interpret human emotional signals and react appropriately.
Another possibility is that our understanding of the nature of AI is evolving, and we’re starting to see it as a tool to augment our abilities rather than merely simulate them.
If this is the case, we may become less concerned with building systems that “appear” human to us and more focused on ones that can do things we can’t do.
However, until this situation is resolved, we can be thankful that the phenomenon of the uncanny valley gives us one more reason to pause and consider what makes us human.
When the lines between the real and the virtual, and the artificial and “natural” are increasingly blurred, highlighting the differences helps us understand the strengths and weaknesses of both.
Related Articles
Flying Taxis And Self-Driving Trucks Arrive In 2026: 6 Transport Trends To Watch
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
Technology in Action: My Key Takeaways on How AI and Quantum Are Accelerating Global Transformation
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
The 10 Biggest Consumer Technology Trends Of 2026
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
8 AI Ethics Trends That Will Redefine Trust And Accountability In 2026
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
The 7 Banking And Fintech Trends That Will Define 2026
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
The 8 Biggest Healthcare Technology Trends To Watch In 2026
By now, “smart” versions exist of just about every home appliance, gadget and gizmos we can think of. However, manufacturers continue[...]
Sign up to Stay in Touch!
Bernard Marr is a world-renowned futurist, influencer and thought leader in the fields of business and technology, with a passion for using technology for the good of humanity.
He is a best-selling author of over 20 books, writes a regular column for Forbes and advises and coaches many of the world’s best-known organisations.
He has a combined following of 4 million people across his social media channels and newsletters and was ranked by LinkedIn as one of the top 5 business influencers in the world.
Bernard’s latest book is ‘Generative AI in Practice’.









Social Media